Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Want to understand how blockchain concepts and related tools are becoming a link between business and technology? And how will they benefit your enterprise? Then you’ve landed at just the right place. This blog on Hyperledger vs Ethereum will underline the differences between two highly sought-after blockchain platforms. Then you can decide for yourself which among these two is better-suited for catering to your requirements.
Hyperledger vs Ethereum
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is an open-source distributed public blockchain network. It allows decentralized apps to be built on it with the help of Smart Contract functionality.
Vitalik Buterin developed Ethereum as an extension to the original core blockchain concept. He improvised Bitcoin’s protocols to support applications beyond currency issuance. Its major breakthrough is the ability to easily write and deploy Smart Contracts. These are actually bits of code that are executed on the network. Hence, this platform could help developers to write programs for building decentralized organisations.
Anyone across the globe can connect with Ethereum blockchain and can maintain the current state of the network. Therefore, Ethereum is also widely referred to as the “World Computer”.
What is Hyperledger?
“Hyperledger is an open source development project to benefit an ecosystem of Hyperledger based solution providers and users. It is focused on blockchain related use cases that will work under a variety of industrial sectors.“ – Brian Behlendorf (Executive Director, Hyperledger)
Every business and industry is distinctive in their own way and the applications serving to their needs must be personalized. The Ethereum Blockchain works with a very generalized protocol for everything that runs on its network. You can think of Hyperledger, on the other hand, as a software for people to develop their own personalized blockchains tending to the needs of their businesses.
Hyperledger is an open source collaborative project hosted by The Linux Foundation. It is neither a tool nor a platform like Ethereum. It’s an umbrella strategy with multiple platforms for developing enterprise solutions.
Now that you know what Hyperledger and Ethereum are, let’s compare on what grounds they differ and how they serve different purposes.
Hyperledger vs Ethereum: Key Differences
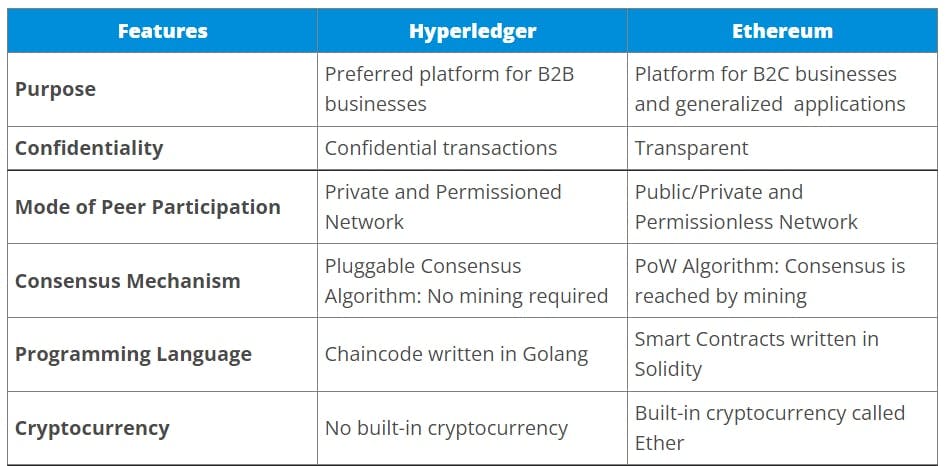
Purpose: The most essential distinction between Hyperledger and Ethereum is the intent they are designed for.
Ethereum runs the Smart Contracts on the EVM for applications that are attributed to being decentralized and are for mass consumption.
On the other hand, Hyperledger leverages blockchain technology for business. It is designed to support pluggable implementations of components delivering high degrees of confidentiality, resilience, and scalability. Hyperledger has a modular architecture and provides a lot of flexibility in how you want to use it. Its extensible architecture provides futuristic solutions for enterprise blockchains.
Confidentiality:
Let’s say Andy runs a pie manufacturing industry on the blockchain.
Through Hyperledger, it is possible for Andy to sell pies to Bobby at a discounted price while keeping their agreement confidential from Andy’s other customers.
Such an arrangement would not be possible if Andy was using Ethereum for the same. Because Ethereum is absolutely transparent and every transaction is visible to everyone on the network.
Thus, Hyperledger allows confidential transactions. Consequently, it gives businesses the flexibility and security to make transactions visible to select parties having correct encryption keys.
Ethereum can be either public or private without any permissions whereas Hyperledger is a private and permissioned network.
This means that in Ethereum, anybody can participate in the network at any time. But Hyperledger has a predefined community of participants, and access to the network is restricted only to them. One requires permission to join the network. This mode of participation has a profound impact on how consensus is reached.
Consensus Mechanism:
With Ethereum, all the network participants (or nodes) have to reach consensus over all the transactions. This is irrespective of whether a node takes part in a particular transaction or not. Presently, Ethereum’s establishes its consensus mechanism by mining based on the Proof-of-Work (PoW) algorithm. All the nodes have to agree upon a common ledger and all of them have access to all entries ever recorded.
In contrast, Hyperledger allows nodes to choose between No-op (no consensus needed) and an agreement protocol (PBFT) whereby two or more parties can agree on a key in such a way that both influence the outcome. This precludes undesired third parties from forcing a key choice on the agreeing parties. Thus, Hyperledger has a fine-grained control over consensus and restricted access to transactions which results in improved performance scalability and privacy.
Programming Language:
Another key difference is the use of Smart contracts in Ethereum, written in a high-level contract-oriented language called Solidity.
However, in Hyperledger you can use the term “chaincode” as a synonym for smart contract. A chaincode typically handles business logic agreed to by members of the network, so it may be considered as a smart contract. These chaincodes are written in Golang, a programming language created by Google.
Cryptocurrency:
Hyperledger doesn’t require cryptocurrencies for transactions. It doesn’t have a built-in native cryptocurrency like Ethereum’s token, Ether. Hence, there is no requirement of mining at all. This allows for scalable consensus algorithm that is capable of handling high transaction rates required by most enterprise applications. But, looking at both sides of the coin (or token, eh?) since Ethereum has its own ether, it can be advantageous over Hyperledger in the use cases which require a cryptocurrency.
Since Hyperledger is also programmable, it can leverage the embedded logic in chaincode to automate business processes across your network. You could also develop custom tokens via chaincode, if required.
Which one should you go for?
At a practical level, developers who want to build an application or start an industry on such platforms, have to make a choice. Hyperledger and Ethereum, both are highly flexible, but in different aspects.
Ethereum’s powerful smart contracts engine makes it a generic platform for literally any kind of application. However, its permissionless mode of operation and total transparency comes at the cost of performance scalability and privacy.
Hyperledger solves performance scalability and privacy issues by permissioned mode of operation and fine-grained access control. Further, the modular architecture allows Hyperledger to be customized to a multitude of applications, analogous to a toolbox.
Happy Learning!! Please do LIKE and SHARE the article.
